In the UK, a blue panel indicates a dry powder fire extinguisher, making it one of the most versatile and widely used fire safety devices in British workplaces and public buildings. This dry powder fire extinguisher blue panel UK system follows strict British Standard EN 3 regulations, ensuring consistent identification across all fire safety equipment. Understanding this colour coding system is essential for workplace safety, emergency response, and legal compliance. The blue identification panel sits prominently on the red extinguisher body, providing instant recognition during high-stress emergency situations when quick decision-making can mean the difference between containing a fire and facing a major incident.
UK Fire Extinguisher Colour Coding System
The fire extinguisher colour coding British standard follows a systematic approach designed for rapid identification during emergencies. All fire extinguishers in the UK feature a red body with coloured panels indicating their specific type and application.
This standardised system replaced the old method where entire extinguisher bodies were painted different colours. The modern approach maintains visual consistency while providing clear type identification through coloured zones above the operating instructions.
| Medium | Panel colour | Main fire classes | Typical locations | Avoid use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Red panel on red body | A | Offices classrooms corridors | Liquids gases and live electrical |
| Foam | Cream panel | A B | Garages retail fuel stores | Live electrical unless rated |
| Dry powder | Blue panel | A B C electrical | Workshops forecourts plant rooms vehicles | Enclosed rooms due to inhalation and visibility issues |
| CO2 | Black panel | Electrical B | Server rooms switch rooms kitchens | Confined spaces without ventilation and Class A deep seated |
| Wet chemical | Yellow panel | F A | Commercial kitchens fryers | Electrical unless combined rating and non cooking risks |
Blue Panel Identification Standards
The ABC dry powder extinguisher identification system uses blue panels specifically to denote multi-purpose dry chemical extinguishers. These blue markers must be positioned prominently on the extinguisher body, typically above the operating instructions label.
British Standard EN 3 mandates specific blue colour specifications, ensuring consistency across all manufacturers. The blue panel should be clearly visible from multiple angles and remain legible even in low-light emergency conditions.
This standardisation means that whether you encounter a dry powder extinguisher in a London office building, Manchester warehouse, or Edinburgh retail store, the blue fire extinguisher dry powder type will always display the same distinctive blue identification panel.
What Makes Dry Powder Extinguishers Special?
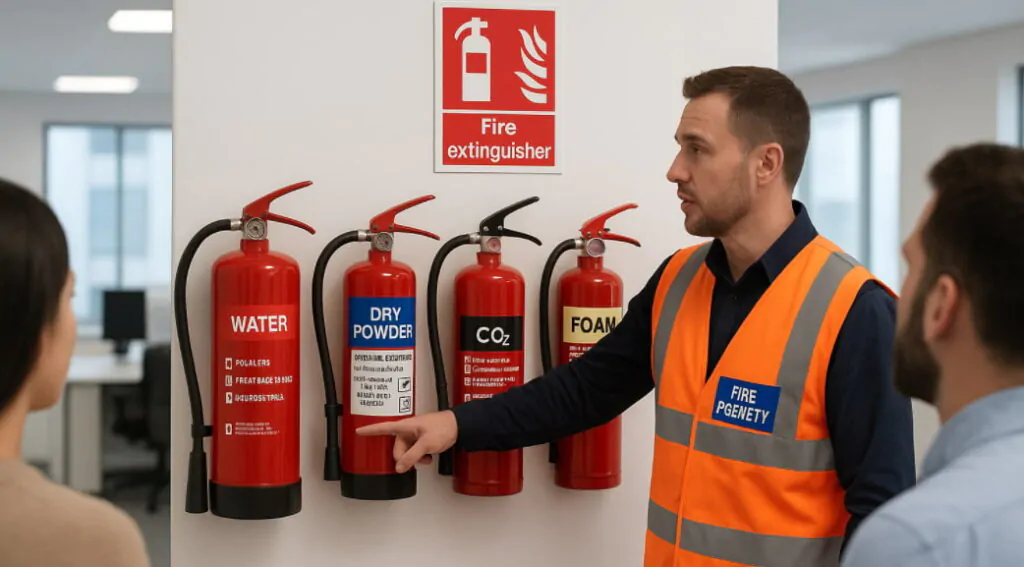

Dry powder extinguishers earn their reputation as the most versatile fire-fighting tools available in the UK. The UK fire safety extinguisher colours system designates blue panels for these devices because they handle multiple fire classes effectively.
These extinguishers contain monoammonium phosphate powder that interrupts the chemical chain reaction sustaining fires. When discharged, the powder creates a blanket effect that separates fuel from oxygen while simultaneously cooling burning materials.
The powder remains effective across temperature ranges commonly encountered in British climates, from cold Scottish winters to warm southern English summers. This reliability makes dry powder extinguishers suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Fire Classes and Applications
Understanding which fires require dry chemical fire extinguisher colour UK coded equipment helps ensure proper emergency response. Dry powder extinguishers effectively combat three main fire classes.
Class A fires involve ordinary combustible materials such as wood, paper, textiles, and plastics. These represent the most common workplace fires in offices, retail environments, and manufacturing facilities.
Class B fires encompass flammable liquids including petrol, oil, paint, and solvents. Industrial sites, garages, and chemical storage areas frequently require protection against these hazards.
Class C fires involve flammable gases such as propane, butane, and natural gas. Kitchen environments, heating systems, and industrial processes often present these risks.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance
The fire extinguisher panel colours regulations form part of comprehensive UK fire safety legislation. The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 requires responsible persons to ensure appropriate fire-fighting equipment is available and properly maintained. Workplace fire risk assessments must consider the types of fires likely to occur and specify suitable extinguisher types accordingly. Many assessments recommend dry powder extinguishers due to their multi-class capabilities.
British Standard BS 5306 provides detailed guidance on extinguisher selection, installation, and maintenance requirements. Compliance with these standards often influences insurance coverage and liability considerations.
Installation and Positioning Guidelines
Proper placement of blue-panelled dry powder extinguishers requires careful consideration of workplace layouts and fire risks. Fire safety equipment identification colours serve little purpose if extinguishers are poorly positioned or obscured from view. Extinguishers should be mounted at consistent heights, typically between 1.5 and 2 metres from floor level. Clear sight lines and unobstructed access paths ensure emergency responders can locate and retrieve equipment quickly.
Signage indicating extinguisher locations must complement the blue panel identification system. Photoluminescent signs remain visible during power failures, while directional arrows guide users toward equipment locations.
Maintenance and Inspection Requirements
British standard fire extinguisher coding extends beyond initial installation to encompass ongoing maintenance responsibilities. Annual servicing by competent technicians ensures extinguishers remain functional when needed.
Monthly visual inspections should verify that blue panels remain clearly visible and undamaged. Pressure gauges, safety seals, and discharge instructions require regular checking to maintain operational readiness. Record keeping demonstrates compliance with legal obligations and provides audit trails for insurance purposes. Documentation should include service dates, inspection results, and any remedial actions taken.
Training and User Education
Effective use of dry powder extinguishers requires proper training that goes beyond simply recognising blue panels. Users must understand the PASS technique: Pull, Aim, Squeeze, and Sweep for optimal fire suppression results.
Training programs should emphasise when not to attempt fire-fighting, prioritising personal safety over property protection. Escape route planning and emergency service notification procedures form essential components of comprehensive fire safety education. Regular refresher training helps maintain competency levels and reinforces the importance of the colour coding system during high-stress emergency situations.
Quick checklist for on site recognition
- Look for a red body with a blue identification panel and the words Dry Powder or ABC Powder
- Confirm the fire classes on the front pictograms and text
- Check the pressure gauge if fitted and the maintenance tag date
- Position near likely risks yet clear of obstructed corners
- Keep signage visible and not hidden behind furniture
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a blue panel on a fire extinguisher mean in the UK? A blue panel indicates a dry powder fire extinguisher, which is suitable for Class A (solids), Class B (liquids), and Class C (gases) fires. This follows British Standard EN 3 colour coding regulations.
Can I use a blue-panelled extinguisher on electrical fires? While dry powder extinguishers can be used on electrical equipment, you should switch off the power first if safely possible. They’re not specifically designed for electrical fires like CO2 extinguishers with black panels.
Are blue fire extinguisher panels the same throughout the UK? Yes, the blue colour coding for dry powder extinguishers is standardised across England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland under British Standard EN 3.
How often should dry powder extinguishers be serviced? UK regulations require annual servicing by qualified technicians, plus monthly visual inspections by responsible persons to ensure the blue identification panel and equipment remain in good condition.
What’s the difference between blue and black panelled extinguishers? Blue panels indicate dry powder extinguishers for solid, liquid, and gas fires, while black panels denote CO2 extinguishers primarily designed for electrical equipment and flammable liquid fires.
Where should blue-panelled extinguishers be positioned in buildings? They should be easily accessible, clearly visible, mounted at appropriate heights, and positioned near high-risk areas while maintaining clear escape routes for users.
References:
- Surrey Fire: Fire Extinguisher Colours Guide – https://surreyfire.co.uk/fire-extinguisher-colours/
- Fire Safe: Portable Fire Extinguisher General Information – https://www.firesafe.org.uk/portable-fire-extinguisher-general/
- Derbyshire Fire and Rescue Service: Fire Extinguishers Guidance – https://www.derbys-fire.gov.uk/safety/business/guidance-and-advice/fire-extinguishers
Article Summary
In UK settings, the blue identification panel marks a dry powder extinguisher. The red body with a blue band follows BS EN 3 practice that replaced older full body colours. ABC powder covers A, B, and C classes and may be used on live electrical equipment with care, yet it is usually avoided in enclosed rooms due to residue and visibility. Always match extinguisher type to risk and train teams to recognise colour panels and class symbols.